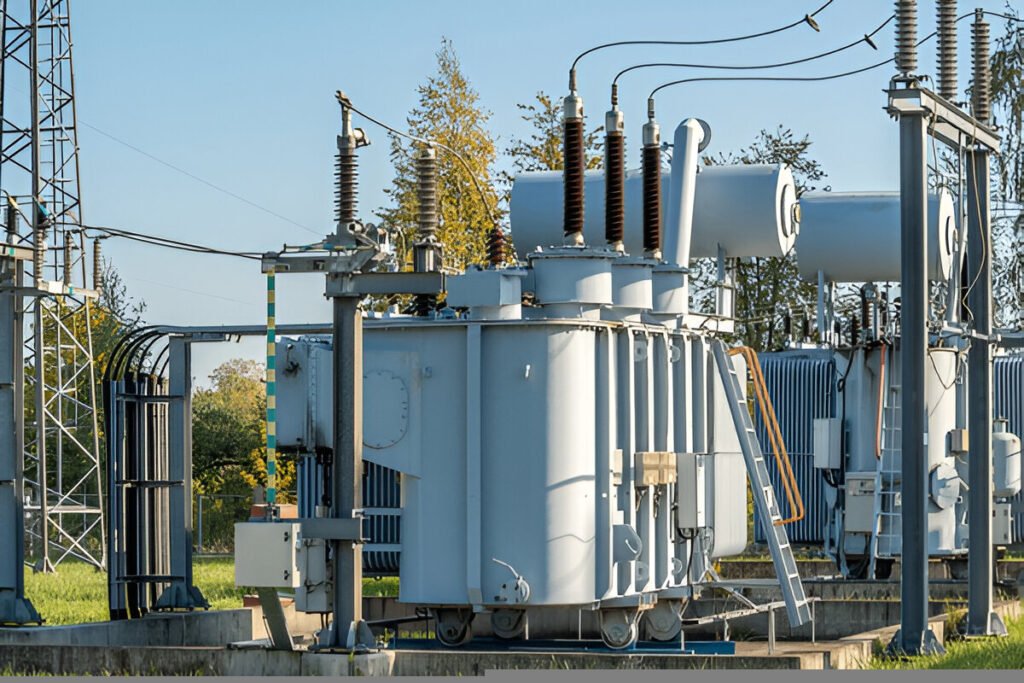
How Different Kinds of Transformers Respond to Power Surges and How to Protect Them
Power surges are one of the most common causes of electrical damage to transformers and can drastically impact their performance and longevity. Whether you’re using kinds of transformers for industrial, commercial, or residential applications, understanding how power surges affect these critical components is essential for ensuring their long-term reliability.
A power surge occurs when there is a sudden increase in voltage that exceeds the normal operating level of the electrical system. This can happen due to lightning strikes, sudden changes in electrical load, or faulty equipment. In this post, we’ll dive into how power surges impact transformers, the different types of transformers and their responses, and strategies for preventing surge-related damage.
What is a Power Surge?
A power surge, also known as a voltage spike or transient voltage, is a brief and rapid increase in voltage that typically lasts for a fraction of a second. Surges can cause serious issues for electrical systems, especially transformers, by overloading their components and causing insulation failure, overheating, or even catastrophic failure.
Power surges can occur for several reasons, such as:
- Lightning strikes: Lightning can induce surges through direct strikes or nearby strikes.
- Switching transients: Sudden switching of electrical loads or equipment (like motors or large machines) can cause voltage fluctuations.
- Faulty equipment: Poorly maintained or malfunctioning electrical devices can introduce surges into the system.
Understanding these causes is key to mitigating damage to your transformer systems.
How Power Surges Impact Different Kinds of Transformers
1. Oil-Filled Transformers
Oil-filled transformers are some of the most commonly used kinds of transformers due to their excellent insulation and cooling properties. However, these transformers are vulnerable to power surges, especially when surge protection mechanisms are not in place.
When a surge occurs, the excess voltage can:
- Break down insulation: High-voltage surges can cause the oil’s insulating properties to degrade, leading to insulation failure and increased risk of short circuits.
- Overload the system: Surge currents can overload the transformer’s winding, potentially causing overheating and damage to the windings or core.
- Increase the risk of fire: In extreme cases, surges can cause the oil to ignite, leading to hazardous fires.
To protect oil-filled transformers, it’s essential to have proper surge protection devices (SPDs) installed and perform regular maintenance.
2. Dry-Type Transformers
Dry-type transformers, which use air as an insulating medium instead of oil, are common in commercial and residential applications. While they are safer in terms of fire risk, they are still susceptible to power surges.
Effects of Power Surges on Dry-Type Transformers:
- Internal arcing: Surges can cause internal arcing between windings, leading to insulation breakdown and potential failure.
- Component damage: The sudden surge of electricity can overheat internal components, reducing the transformer’s lifespan.
- Premature aging: Repeated exposure to power surges can accelerate the aging of insulation materials and cause early failure.
Dry-type transformers can benefit from surge protection systems that limit the voltage spikes and protect their sensitive components.
3. Distribution Transformers
Distribution transformers are used to step down voltage levels for local distribution and are often exposed to a variety of electrical stresses, including power surges.
Impact of Power Surges on Distribution Transformers:
- Voltage regulation problems: Power surges can cause temporary instability in voltage levels, leading to poor regulation and inconsistent power delivery.
- Damage to switching equipment: The surge can damage the transformers’ circuit breakers and protection relays, which are vital for maintaining safe operations.
- Premature wear: Like other kinds of transformers, repeated surge events can cause premature wear on windings and insulation.
As distribution transformers are critical for delivering power to end users, surge protection is essential for maintaining reliability and avoiding costly repairs.
Preventing Damage from Power Surges
While power surges can be harmful to kinds of transformers, there are several ways to protect your equipment from surge-related damage.
1. Install Surge Protection Devices (SPDs)
One of the most effective methods for protecting transformers from power surges is to install surge protection devices at key points in the electrical system. These devices act as barriers that absorb or divert excess voltage, preventing it from reaching sensitive equipment like transformers.
2. Proper Grounding Systems
Grounding is essential for ensuring that electrical surges have a safe path to dissipate. Without proper grounding, a surge can cause irreparable damage to transformers. Regular grounding checks should be part of routine transformer maintenance service to ensure the system is safe.
3. Overcurrent Protection
Incorporating overcurrent protection mechanisms into the transformer’s design, such as fuses or circuit breakers, can help protect against prolonged surges. These devices disconnect the transformer from the power source when excessive voltage is detected.
4. Regular Inspection and Maintenance
Routine inspection and maintenance can help detect early signs of transformer wear or weakness. Regular oil testing, insulation checks, and thermal imaging can help identify potential issues caused by surges and allow for proactive repairs before serious damage occurs.
5. Remote Monitoring and Diagnostics
For critical transformers, especially in industrial settings, consider installing monitoring systems that can track performance in real-time. These systems can alert operators to voltage fluctuations or damage caused by power surges, allowing for immediate corrective action.
What to Do If Your Transformer Is Damaged by a Power Surge
If your transformer has already suffered damage due to a power surge, it’s important to act quickly to prevent further issues. Here are the steps you should take:
- Stop operation immediately: If you suspect damage, shut down the system to avoid exacerbating the problem.
- Inspect for visible damage: Look for signs such as burnt components, oil leaks, or scorched insulation.
- Call a professional: Contact a certified transformer company for a thorough inspection and repair services.
In some cases, it may be more cost-effective to replace the damaged transformer with a new or used transformer, especially if the damage is severe.
Conclusion
Power surges are a serious threat to the reliable performance of kinds of transformers, whether they’re oil-filled, dry-type, or distribution transformers. Understanding how these surges affect transformer functionality is key to preventing damage and ensuring long-term reliability.
By installing surge protection devices, maintaining proper grounding, and monitoring transformer health, you can significantly reduce the risk of power surge damage. Whether you’re managing a transformer on-site or purchasing a transformer for sale, taking proactive steps to protect your equipment is essential for maintaining safe and efficient operations.
Need help with your transformer systems?
Reach out to JJ Transformers for expert guidance, surge protection solutions, or transformer repair services.