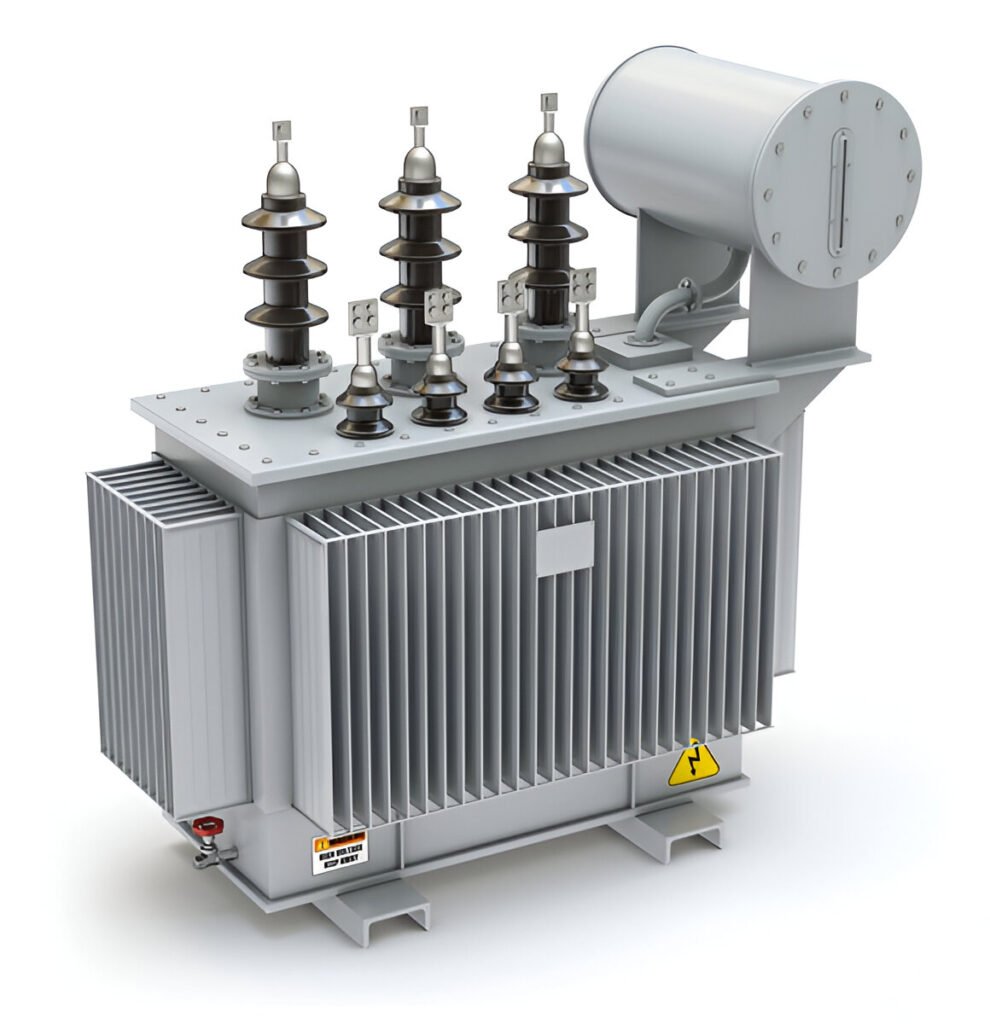
When you’re considering a transformer to buy, efficiency is likely one of your top priorities. And while many factors affect transformer performance—like core material, winding design, and load handling—one often overlooked yet critical component is the cooling system.
In this blog, we’ll explore how transformer cooling systems impact efficiency, performance, and longevity, and why understanding cooling mechanisms is crucial when selecting the right transformer to buy for your business or facility.
Why Transformer Cooling Matters
Transformers generate heat as a byproduct of electrical losses. These losses include:
- Core losses (iron losses) due to magnetic fields
- Copper losses from resistance in windings
If not managed properly, this heat can:
- Accelerate insulation aging
- Reduce operational lifespan
- Increase the risk of breakdowns
- Decrease energy efficiency
This is where cooling systems come in—they regulate temperature, improve energy performance, and ensure safety during prolonged operation.
Types of Transformer Cooling Systems
Depending on the transformer’s size, application, and environment, different cooling systems may be used. When evaluating a transformer to buy, understanding these types will help you choose one that suits your needs.
1. Air Natural (AN) / Dry-Type Cooling
Used in dry-type transformers, this system relies on ambient air for heat dissipation. Fans may be added in Air Forced (AF) versions for enhanced cooling.
Best For: Indoor installations, schools, hospitals, and places with strict fire safety standards.
2. Oil Natural Air Natural (ONAN)
This is the most common method in oil-immersed transformers. Heat is transferred from windings to the oil, and then to the tank walls where it dissipates into the air.
Best For: Medium-sized power applications with moderate loads.
3. Oil Natural Air Forced (ONAF)
Similar to ONAN but includes forced air (fans) for better cooling capacity. Used when load increases temporarily or when better heat dissipation is needed.
Best For: Industrial settings or substations where load may vary.
4. Oil Forced Water Forced (OFWF)
In high-capacity or critical power systems, this method circulates oil and cools it using water through heat exchangers. It provides exceptional thermal management.
Best For: Large substations, power plants, or high-performance industrial sites.
How Cooling Affects Transformer Efficiency
When comparing different options for a transformer to buy, cooling systems directly influence:
- Energy Efficiency: A well-cooled transformer experiences fewer losses due to lower operating temperatures.
- Load Capacity: Improved cooling allows for higher load handling without thermal degradation.
- Lifespan: Reduced thermal stress extends insulation life and delays major repairs or replacements.
- Reliability: Prevents overheating, reducing risks of fire, oil degradation, or catastrophic failure.
Cooling doesn’t just preserve your transformer—it enhances its performance under real-world operating conditions.
Key Considerations When Choosing a Transformer to Buy
Here’s what to evaluate in terms of cooling when selecting a transformer to buy:
- Operating Environment: Is it indoors, outdoors, in a dusty or humid location?
- Load Profile: Will it carry a steady or fluctuating load?
- Noise and Ventilation: Dry-type cooling systems are quieter but may need airflow space.
- Maintenance Capability: Oil-based systems require regular monitoring of fluid quality and radiator cleanliness.
- Cost and Energy Efficiency: Systems with fans and pumps consume additional power but may improve long-term ROI.
If you’re upgrading or expanding, reliable used transformers with high-quality cooling systems can be an excellent option to save costs without compromising performance.
Can Cooling Systems Be Upgraded?
Yes. In many cases, transformer cooling systems can be retrofitted or enhanced. For example:
- Adding radiator fans for ONAN to convert it into ONAF
- Installing temperature monitoring devices for better control
- Replacing old cooling pumps in OFWF systems with high-efficiency models
If you’re working with transformer services providers, they can assess your transformer’s cooling performance and recommend custom improvements.
Selling or Replacing Old Transformers with Inefficient Cooling?
If your existing transformer runs hot, frequently trips, or shows signs of insulation wear, it might be time for a replacement. You can sell transformers that are no longer efficient and switch to newer or refurbished units with better cooling.
Looking for a budget-friendly solution? Second hand transformers that have been inspected and tested can give you the efficiency you need at a fraction of the cost of new equipment.
Where to Find the Right Transformer to Buy
Whether you’re looking for dry-type or oil-immersed transformers with efficient cooling systems, working with a reputable transformer company is key.
At JJ Transformers, we help clients:
- Evaluate cooling performance for their site
- Recommend suitable types of transformers
- Offer high-quality surplus transformers for budget-conscious buyers
- Guide customers through installation and ongoing service needs
We make it easy to find the perfect transformer to buy—whether you need it for a plant expansion, a replacement, or an energy efficiency upgrade.
Final Thoughts
Transformer cooling systems are not just add-ons—they’re essential to maintaining performance, efficiency, and safety. When choosing a transformer to buy, consider the type of cooling system just as seriously as voltage rating, kVA, or brand.
A well-cooled transformer runs better, lasts longer, and saves money over time.
Need help selecting the right transformer with the best cooling configuration? Contact JJ Transformers for expert advice and a wide range of new and used transformers ready to meet your unique operational demands.